Page 30 - Annual Report_21-22
P. 30
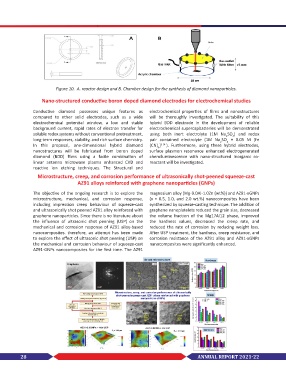
Figure 10. A. reactor design and B. Chamber design for the synthesis of diamond nanoparticles.
Nano-structured conductive boron doped diamond electrodes for electrochemical studies
Conductive diamond possesses unique features as electrochemical properties of films and nanostructures
compared to other solid electrodes, such as a wide will be thoroughly investigated. The suitability of this
electrochemical potential window, a low and stable hybrid BDD electrode in the development of reliable
background current, rapid rates of electron transfer for electrochemical supercapbatteries will be demonstrated
soluble redox systems without conventional pretreatment, using both inert electrolyte (1M Na SO ) and redox
2
4
long-term responses, stability, and rich surface chemistry. pair contained electrolyte (1M Na SO + 0.05 M [Fe
2
4
In this proposal, one-dimensional hybrid diamond (CN) ] 3-/4- ). Furthermore, using these hybrid electrodes,
6
nanostructures will be fabricated from boron doped surface plasmon resonance enhanced electrogenerated
diamond (BDD) films using a facile combination of chemiluminescence with nano-structured inorganic co-
linear antenna microwave plasma enhanced CVD and reactant will be investigated.
reactive ion etching techniques. The Structural and
Microstructure, creep, and corrosion performance of ultrasonically shot-peened squeeze-cast
AZ91 alloys reinforced with graphene nanoparticles (GNPs)
The objective of the ongoing research is to explore the magnesium alloy (Mg-9.0Al-1.0Zn (wt%)) and AZ91-xGNPs
microstructure, mechanical, and corrosion response, (x = 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 wt.%) nanocomposites have been
including impression creep behaviour of squeeze-cast synthesized by squeeze-casting technique. The addition of
and ultrasonically shot peened AZ91 alloy reinforced with graphene nanoplatelets reduced the grain size, decreased
graphene nanoparticles. Since there is no literature about the volume fraction of the Mg17Al12 phase, improved
the influence of ultrasonic shot peening (USP) on the the hardness values, decreased the creep rate, and
mechanical and corrosion response of AZ91 alloy-based reduced the rate of corrosion by reducing weight loss.
nanocomposites. therefore, an attempt has been made After USP treatment, the hardness, creep resistance, and
to explore the effect of ultrasonic shot peening (USP) on corrosion resistance of the AZ91 alloy and AZ91-xGNPs
the mechanical and corrosion behaviour of squeeze-cast nanocomposites were significantly enhanced.
AZ91-GNPs nanocomposites for the first time. The AZ91
28 ANNUAL REPORT 2021-22