Page 36 - Annual Report_21-22
P. 36
PROCESS ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION
Toxic Chromium ions removal from water systems using low-cost mineral adsorbents
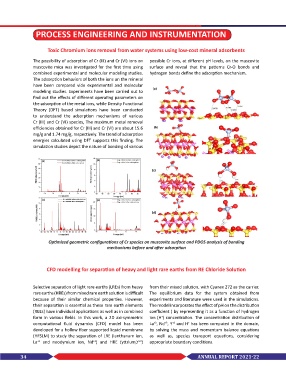
The possibility of adsorption of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) ions on possible Cr ions, at different pH levels, on the muscovite
muscovite mica was investigated for the first time using surface and reveal that the patterns Cr-O bonds and
combined experimental and molecular modeling studies. hydrogen bonds define the adsorption mechanism.
The adsorption behaviors of both the ions on the mineral
have been compared vide experimental and molecular
modeling studies. Experiments have been carried out to
find out the effects of different operating parameters on
the adsorption of the metal ions, while Density Functional
Theory (DFT) based simulations have been conducted
to understand the adsorption mechanisms of various
Cr (III) and Cr (VI) species, The maximum metal removal
efficiencies obtained for Cr (III) and Cr (VI) are about 15.6
mg/g and 1.74 mg/g, respectively. The trend of adsorption
energies calculated using DFT supports this finding. The
simulation studies depict the nature of bonding of various
Optimized geometric configurations of Cr species on muscovite surface and PDOS analysis of bonding
mechanisms before and after adsorption
CFD modelling for separation of heavy and light rare earths from RE Chloride Solution
Selective separation of light rare earths (LREs) from heavy from their mixed solution, with Cyanex 272 as the carrier.
rare earths (HREs) from mixed rare earth solution is difficult The equilibrium data for the system obtained from
because of their similar chemical properties. However, experiments and literature were used in the simulations.
their separation is essential as these rare earth elements The model incorporates the effect of pH on the distribution
(REEs) have individual applications as well as in combined coefficient ( by representing it as a function of hydrogen
form in various fields. In this work, a 2D axi-symmetric ion (H ) concentration. The concentration distribution of
+
computational fluid dynamics (CFD) model has been La , Nd , Y and H has been computed in the domain,
+3
+3
+3
+
developed for a hollow fiber supported liquid membrane by solving the mass and momentum balance equations
(HFSLM) to study the separation of LRE (lanthanum ion, as well as, species transport equations, considering
La and neodymium ion, Nd ) and HRE (yttrium,Y ) appropriate boundary conditions.
+3
+3
+3
34 ANNUAL REPORT 2021-22