Page 53 - Annual Report_21-22
P. 53
Figure: (a) Removal efficiency [inset: time-dependent snapshots of hexane I solution (10 mL, 100 µM) after adding MeO-
2
CTF600 (5.0 mg)]. Time-dependent UV-Vis spectra of hexane solution of iodine (100 µM) after adding MeO-CTF600 (5.0 mg).
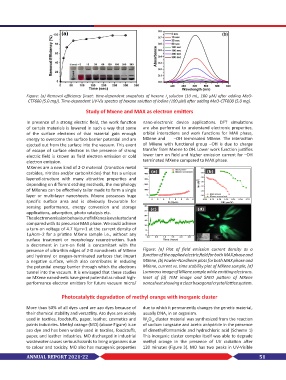
Study of Mxene and MAX as electron emitters
In presence of a strong electric field, the work function nano-electronic device applications. DFT simulations
of certain materials is lowered in such a way that some are also performed to understand electronic properties,
of the surface electrons of that material gain enough orbital interactions and work functions for MAX phase,
energy to overcome the surface barrier potential and are MXene and –OH terminated MXene. The interaction
ejected out from the surface into the vacuum. This event of MXene with functional group –OH is due to charge
of escape of surface electron in the presence of strong transfer from Mxene to OH. Lower work function justifies
electric field is known as field electron emission or cold lower turn on field and higher emission current for –OH
electron emission. terminated MXene compared to MAX phase.
MXenes are a new kind of 2-D material (transition metal
carbides, nitrides and/or carbonitrides) that has a unique
layered-structure with many attractive properties and
depending on different etching methods, the morphology
of MXenes can be effectively tailor made to form a single
layer or multi-layer nanosheets. Mxene possesses huge
specific surface area and is obviously favourable for
sensing performance, energy conversion and storage
applications, adsorption, photo catalysis etc.
The electron emission behaviour of MXenes is evaluated and
compared with its precursor MAX phase. We could achieve
a turn-on voltage of 4.7 Vμm−1 at the current density of
1µAcm−2 for a pristine MXene sample i.e., without any
surface treatment or morphology reconstruction. Such
a decrement in turn-on field is concomitant with the
presence of ultra-thin edges of 2-D nanosheets of MXene Figure: (a) Plot of field emission current density as a
and hydroxyl or oxygen-terminated surfaces that impart function of the applied electric field for both MAX phase and
a negative surface, which also contributes in reducing MXene, (b) Fowler-Nordheim plots for both MAX phase and
the potential energy barrier through which the electrons MXene, current vs. time stability plot of MXene sample, (d)
tunnel into the vacuum. It is envisaged that these studies Luminous image of MXene sample while emitting electrons.
on MXene nanosheets have great potential as robust high- Inset of (d) TEM image and SAED pattern of MXene
performance electron emitters for future vacuum micro/ nanosheet showing a clear hexagonal crystal lattice system.
Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange with inorganic cluster
More than 50% of all dyes used are azo dyes because of due to which it permanently changes the genetic material,
their chemical stability and versatility. Azo dyes are widely usually DNA, in an organism.
used in textiles, foodstuffs, paper, leather, cosmetics and W O cluster material was synthesized from the reaction
19
6
paints industries. Methyl orange (MO) (above Figure) is an of sodium tungstate and acetic anhydride in the presence
azo dye and has been widely used in textiles, foodstuffs, of dimethylformamide and hydrochloric acid (Scheme 1)
paper, and leather industries. MO discharged in industrial This inorganic cluster complex itself was able to degrade
wastewater causes serious hazards to living organisms due methyl orange in the presence of UV radiation after
to colour and toxicity. MO also has mutagenic properties 120 minutes (Figure 3). MO has two peaks in UV-Visible
ANNUAL REPORT 2021-22 51