Page 82 - Annual Report_21-22
P. 82
CENTRAL CHARACTERIZATION
Photofunctional materials for industrial dye mineralisation
The main objective of the project is to develop a process Ascorbic acid by the hydrothermal process to form a
for the textile industries to treat their waste water carbon based layered double hydroxide (LDH) composite
before discharging it. It also includes, the use of treated for the complete mineralization process under solar light/
water in agriculture, washing or further dyeing after visible light. The samples were studied and characterized
proper analysis of the treated water. In order to achieve for their photocatalytic activity toward mineralization of
the objective, we, prepared hydrothermally, a series conventional, reactive, and textile dyes (cationic, anionic
of photofunctional materials with different carbon and mixed).
precursors Ca. Sucrose, Kitchen Sugar, Citric acid, and
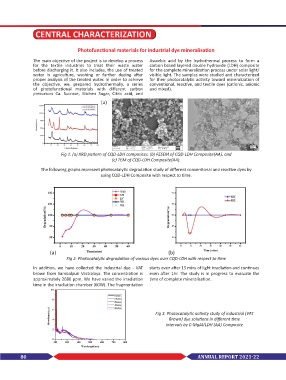
(a) (b) (c)
Fig 1. (a) XRD pattern of CQD-LDH composites, (b) FESEM of CQD-LDH Composite(AA), and
(c) TEM of CQD-LDH Composite(AA).
The following graphs represent photocatalytic degradation study of different conventional and reactive dyes by
using CQD-LDH Composite with respect to time.
( a ) ( b )
Fig 2. Photocatalytic degradation of various dyes over CQD-LDH with respect to time
In addition, we have collected the industrial dye - VAT starts even after 15 mins of light irradiation and continues
brown from Sambalpuri Vastralaya. The concentration is even after 1hr. The study is in progress to evaluate the
approximately 2680 ppm. We have varied the irradiation time of complete mineralisation.
time in the irradiation chamber (60W). The fragmentation
Fig 3. Photocatalytic activity study of industrial (VAT
Brown) dye solutions in different time
intervals by C-MgAl/LDH (AA) Composite
80 ANNUAL REPORT 2021-22